Customer data is the foundation of a successful marketing strategy. It is the information a business collects on its consumers when interacting with it online and offline. The retail industry, in particular, is investing heavily in data analytics tools to give their customers personalized experiences and increase sales.
In 2020, global big data analytics generated $4.85 billion for the industry, estimated to hit $25.56 billion by 2028. However, data privacy regulations are strict on how this information is handled. Customers themselves are increasingly concerned about how their data is used. Let's look at how you can leverage the data and balance the interests of your consumers and business.
Why collect customer data?
In a nutshell: More data = Richer insights.
These insights will be the foundation of your marketing strategy. They enable you to plan how you will improve customer experience. Analyzing the data shows your customer’s needs, motivations, and expectations. It allows you to observe behaviors and increase their engagement with your business. You can use this to identify patterns and predict future behavior.
With behavioral and geographic segmentation, you refine your targeting and customer acquisition. That puts you in a position to effectively attract and retain high-value customers who are the right fit for your business, ensuring sustainable growth. As you collect this data, you're responsible for protecting it. Breaches will be costly to your brand, from the reputation hit to the lawsuits you will face. 2022 saw the global average business cost hit $4.35 million per data breach. Here is an in-depth look at how you can collect and protect the data and win the trust of your customers.
Types of consumer data to collect
There are four key categories of data that businesses collect from their customers. This data is needed for day-to-day operations, regulatory requirements, product and service delivery, and business growth planning.
Profile information
It is the data needed to make the customer profile. At a basic level, it includes the name, phone number, and contact information. This Personally Identifiable Information (PII) can also include the driver's license number, date of birth, and credit/debit card details. Depending on the business in question, additional information may be needed, like what the customer does for a living, how much money they make, and their next of kin details. For those in the financial industry, KYC (Know-your-customer) details also include aspects like the social security number and actual photographs of the user, alongside digital copies of their ID card, passport, and tax PIN certificate.
Interaction data
The information is collected when the customer interacts with your business at different touchpoints. It can be website visits, engagement on social media accounts, products purchased on e-commerce stores, and items that have been returned.
Behavioral data
The focus here is the habits of your customers. It can be quantified through website analytics tools, which we will cover shortly. Such data includes devices they use to visit your website and the level of attention they give to the different pages they land on. It also covers when they sign up for free trials, how often they log in to their accounts and records on those that suspend/deactivate their accounts.
Sentiment data
What opinion do customers have about your business? It gives you a picture of your engagement and the quality of your products and services. It includes reviews from customers, responses provided in surveys, and feedback obtained from in-person interactions with the customers. Unlike behavioral, interaction, and personal data, which can be quantified, this sentiment data is more difficult to process. Some customers may give you detailed responses, while others will keep them concise. It falls on the business owner, sales rep, or customer service personnel to extract the relevant information from the reviews and convert it into actionable data.
7 ways to collect customer data
These methods can be used to collect qualitative and quantitative data. Qualitative data gives you more insight from your consumers, e.g., their feedback on your products and services. Quantitative data looks at numerical aspects like sales records and site traffic statistics. Here are tactics you can use to collect data ethically, safely, and legally:
1. Website tracking tools
Installing an analytics tool on your website will collect data on how people use it, and you can integrate this with Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems. Take Google Analytics, for instance. At a basic level, it shows you:
Source of traffic - e.g., did they click through from search results, social media, or a paid banner ad?
Time is taken looking at specific pages
Different pages visited
Network location and IP address
Web browser used
Some extra customization on Google Analytics can get you to see the scroll depth, document your visitors downloaded, errors made when site visitors fill forms, and the interactions they made with site-specific widgets.
This data gives you insight into the behavior of your website’s visitors. It also shows you how your SEO and digital marketing efforts are faring, for you to identify the strategies that are giving you optimal return on investment. That way, you can improve your marketing campaigns to get more conversions to your website.
Another critical website tracking tool is cookies. These store information on customer preferences and login details so that users don't have to spend time filling them in whenever they visit the site, shopping cart items, and browsing history. They can also store personally identifiable information like customer names, home and email addresses, or phone numbers.
2. Customer transaction data
It focuses on the order history of the consumers. Knowing what they have spent money on helps you better understand their behavior. Do they purchase online, on the phone, or in person? How often do they make returns? Does the customer use discount codes or coupons frequently? Where were they located when they made the purchase? Was the purchase made through the website or app., and did they click through from certain links - like search results or ads? It complements information from registration details, cookies, and reward programs as they shop online.
From their transaction history, you can assess the personal spending habits of your customers. It lets you personalize the marketing and even offer higher discounts to long-term customers to retain their loyalty.
When placing orders, the usual fields they fill in include name, phone number, email address, and delivery address. It is needed to complete the delivery and addresses issues arising from the order. Accurate transaction data identifies the customer even when they are using different devices.
3. Email newsletters & blog subscriptions
When people subscribe to your newsletter, you'll get data like the email address at the minimum. You can also include additional information they can provide when signing up - like the products they are most interested in or their demographic (e.g., age range or industry).
For blog signs ups, on the other hand, readers get notified whenever a new post is published. Here, ask for their email address, name, and information like which blog topics they would be more interested in. That way, you can generate more content per your audience's preferences. Your business benefits by providing more personalized services to customers. In turn, your customers get to avoid marketing and updates that they aren't interested in.
4. Surveys
These give you flexible ways to collect data from your potential, current and past customers. For instance, you can collect feedback after customers hire a service, buy a product, or ask about their experience after interacting with your helpdesk. Use surveys to ask for their opinion on your website's navigation. You can even follow up on complaints or dissatisfaction levels for those unsubscribing from your services.
The surveys can be conducted through online forms, text prompts, over the phone, or in person. You can even have pop-up surveys on your website given to users who have spent a particular amount of time on your website. However, surveys tend to be easy to ignore. Here, timing is critical. Avoid sending out surveys too early. Allow your customers to engage with your business or use its products. Give them time to get familiar with it before you ask for feedback. Also, don't want too long afterward since late surveys will be met with disinterest.
5. Promotions & contests
Running competitions and giveaways increases engagement and enriches your database with more consumer information. The lure of freebies encourages people to share their data, such as contact information, that you can use for future marketing campaigns. During the offers, you can also ask participants questions ranging from where they heard about the promotion to which of your products is their favorite. This data can then be used to personalize future communication.
6. Social media
Social media is a data goldmine. From your followers' list, you can see who is interested in your brand. Those engaging with your page, liking and commenting on posts, are either potential or current customers. Those with similar interests with them are your target audience as well. You can see when your audience is most active by looking into demographics like interests, location, and age. Mentions - when someone tags your brand in a post, situations where your hashtag has been used and reviews form part of the qualitative data you can collect from social media. On the quantitative front, this looks at the number of post shares and click-throughs your content has generated. The different social media sites come with audience insights tools to assess your audience. e.g., the Meta Business Suite for Facebook.
7. Customer relationship management (CRM) software
CRM software gives you tools to automatically collect and store a wide range of customer data that you can use to drive engagement, build brand loyalty and increase conversions.
Data you can collect through the CRM include:
Communication details include the customer's name and contact details, preferred mode of contact, and customer acquisition channel, e.g., through social media, ads, or Google search.
Transaction details are the purchase and its value, the purchase time, and the payment methods used.
Engagement details - Which kinds of messages does the customer frequently respond to (e.g., informational or promotional)? Do they respond to emails? CRMs can also be used to record calls made to the customer service team.
Feedback data – Survey results, customer complaints, products that have been returned, as well as ratings and reviews.
Interests - This helps in defining the demographics of your target audience. For instance, location data is collected through the forms customers fill out or through the IP address when they are interacting with your website, as well as hobbies and income levels indicated during surveys. For instance, with Layerise product registration forms, you can customize the data you want to capture during the registration event and match responses to your campaign's communication.
The revolution of data collection: leverage the onboarding process
Companies can collect valuable data about their customers throughout different stages of their relationship. During the onboarding registration process, companies can gather first-party data such as name, email address, demographic data and even behavioural information. This allows them to personalize communications and target specific customer segments more effectively.
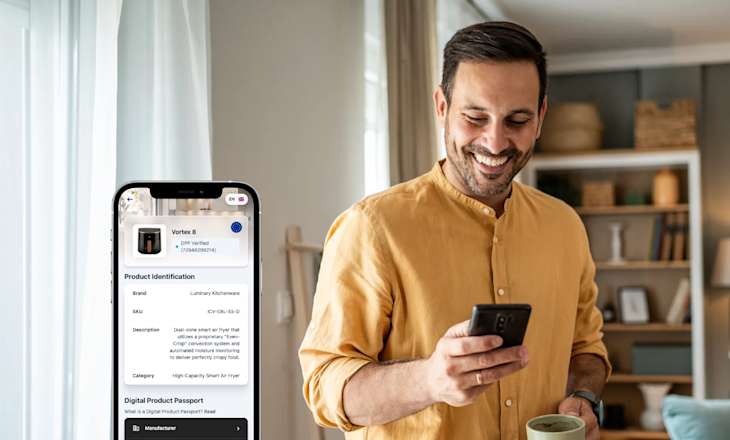
Product registration is an opportunity for companies to collect data. By encouraging customers to register their products, companies can gain insights into the customer experience, identify any issues or areas for improvement, and offer relevant product recommendations.
One solution that can help companies collect and manage customer data effectively is Layerise. Layerise is a software platform that provides tools for customer data capture. It allows companies to create customizable registration forms, capture and store customer data securely, and analyze customer behavior and engagement. With Layerise, companies can better understand their customers and use this knowledge to improve their products and services.
How to turn data into information
It's easy for business owners to get swamped in an ocean of data. Also, data won't help if it is the wrong kind of data or hasn't been adequately compiled and analyzed. How can the data you obtain be transformed into actionable information?
Naturally, the first step is only collecting valuable data, like with Layerise’s 1st party customer data collection tools. Ask whether the data you're compiling is needed to improve your business services or reduce costs. Next, ensure that the data is accurate. After all, you don't want to waste marketing resources on demographics that have been wrongly presented.
Invest in analytics tools to sift through the mounds of data and present it in an easy-to-digest manner. The information here is showcased through dashboards and reports that guide planning for marketing campaigns and business strategies. As AI programs become more efficient in this, they break down the data and refine it to give you actionable insights - and some even go the next step and offer recommendations to your organization’s decision-making team.
GDPR compliance tips
As long as you're handling customer data, you must comply with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). Here are aspects that you should put in place when collecting and managing customer data:
Get clear, explicit consent.
No gray area. Customers must know you will collect, process, and store their data. Ensure that you've allowed them to agree or disagree with the collection - and this consent should be documented. In 2020, the Italian telecom TIM was fined €27.8 million ($30.7 million) for using customer data without consent for marketing purposes, including telemarketing calls. It was also determined that the data was improperly stored and processed, putting it at risk of security breaches.
Data transparency - Make your customers aware of your motives
Your customers should know what data you're collecting, what it will be used for, and how long your organization will store it. Businesses usually display the data collection notification on website forms (note that the consent boxes should not be pre-ticked) and cookie collection notices. Just ensure that the messaging in these notifications is clear and straightforward. You will be struck with a non-compliance fine if you collect data clandestinely. For instance, a website's visitor should give explicit consent before cookies are used and be able to withdraw consent to cookie use. Speaking of which, customers should have access to any collected data and a way to modify or delete it. Google Ireland was fined €60 million for not giving users an easy way to refuse cookies, as GDPR and the ePrivacy Directive required. Google LLC got a €90 million fine since they were deemed jointly responsible, bringing the total hit to the company to €150 million.
Appoint a Data Protection Officer (DPO)
The DPO is in charge of the data protection strategy of your business or organization. This is a mandatory requirement in line with GDPR's Article 37 if your organization regularly and systemically monitors users' data on a large scale, is a public authority, or has 250 or more employees. The processing "at large scale" is ambiguous since the GDPR does not define this, so many originations get DPOs to remain safe.
Verify the age of consent.
Only data of persons at least 16 years old can be collected and processed under GDPR. Consent should be given by their parent or legal guardian. How do you deal with young kids interacting with your website? Implement an age verification process before collecting data.
Map data flow with a GDPR Diary
This records your organization's efforts and programs toward GDPR compliance. First, you identify the data sources, e.g., name and contact information collected for users to download an eBook from your website. Next, you map how this data will be processed through the organization. For instance, the contact information can be collected to create sales leads and stored in a specific database accessible by internal email marketers. Any leads that don't subscribe are deleted after X number of days.
Indicate as much information as possible in the GDPR diary, including identifying instances where sensitive data is collected – even classifying this by its level of sensitivity. IP addresses are also classified as personal data, especially if you can link them to a person's identity. For instance, if you collect their IP with the email, this data can be used to identify them.
Report data breaches immediately
Going by Article 33, any data breaches should be reported within 72 hours. The processor reports the incident to the controller, who reports it to the supervising authority - the Data Protection Association (DPA), which controls GDPR monitoring and enforcement. The DPA is an independent public authority that supervises and investigates how businesses and organizations apply the data protection law and impose non-compliance fines. A GDPR diary will also be helpful in case of a data breach since it will show your organization's progress in improving data security.
Approaches to data collection that build trust
Data privacy laws have put businesses on a short leash. There is strict scrutiny on collecting, analyzing, storing, and sharing customer information. Consumers continue demanding privacy rights, and non-compliance fines hit businesses that ignore their obligations. You can build trust with your consumers by:
Being transparent on compliance and internal data handling processes
Your current and potential customers know that private corporations and government agencies are tracking them. They get livid when data is used without consent and want to live without the fear of intrusion. For instance, a survey showed 51% of Americans are not confident that social media sites are doing enough to protect their data. Being transparent about the data you collect, your respect for it, and your state of compliance will enable customers to trust you more with their data and be comfortable doing business with you.
Give back control to the customer.
While a business collects and stores the data, it still belongs to the individual. Giving customers control over what they do with their data and who can view, access, or change it will increase their trust. At the very least, a detailed audit report should show how, when, and where the data has been used. Implementing data access policies and limitations in your business will also aid in this.
Reassure your customers by periodically sending them emails or notifications showing your business's steps to protect their information from malicious actors. If your customers feel safe, they will trust you more. Layerise enables you to securely collect data from multiple sources and create a unified customer profile, which you can use to personalize your marketing and improve customer experience. Book a demo on the customer data platform to grow your consumer brand.
What are 5 methods you can use to capture customer data?
How will the Customer Information Management tool be used? A company in event marketing has already collected prospect and customer information. ... Registering platform. ... Virtual events platform. . App for mobile events and websites. ... Survey.
What are the 4 types of customer data?
Type customer data. Basic data. Interactions. Data. Statistics of behavior. Attributudinal information.
How do businesses collect customer data?
Almost all businesses ask the customer directly for information about a specific product. If someone logs into a site it's often necessary that the form fill out. Company employees are asked to provide an address, e-mail address, and other demographic details including gender and maybe others.
What is the most common method of collecting user data?
The best methods of collecting primary data are surveys or interviews. Questionnaire collecting enables a researcher to get information about their personal characteristics and attributes.
Is collecting user data legal?
Since most firms do not have any laws regulating personal data, they can simply do whatever they desire. In almost all States, a company may use the information collected from you and share it with you with the company.
Learn how to collect valuable insights on your customers to sell even more.

How to Turn a New Obligation into a Growth with Layerise
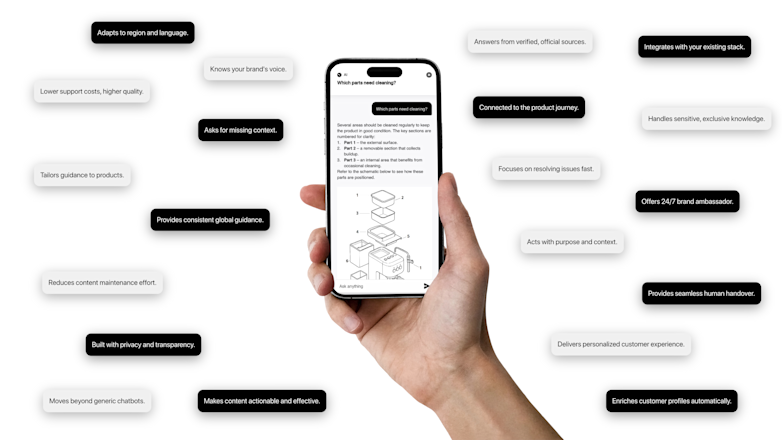
A trusted, brand-safe AI assistant that knows your products, your customers and your content.