In today's interconnected world and conscious consumer landscape, the concepts of transparency and product traceability have evolved from buzzwords to fundamental pillars of business operations, particularly for consumer goods companies. These concepts go beyond market trends; they are the very foundation upon which sustainable practices and responsible business conduct are built.
A clear indication of their importance is the growing acknowledgment by regulatory authorities worldwide of the crucial role that transparency and traceability play in advancing environmental sustainability and ensuring consumer safety.
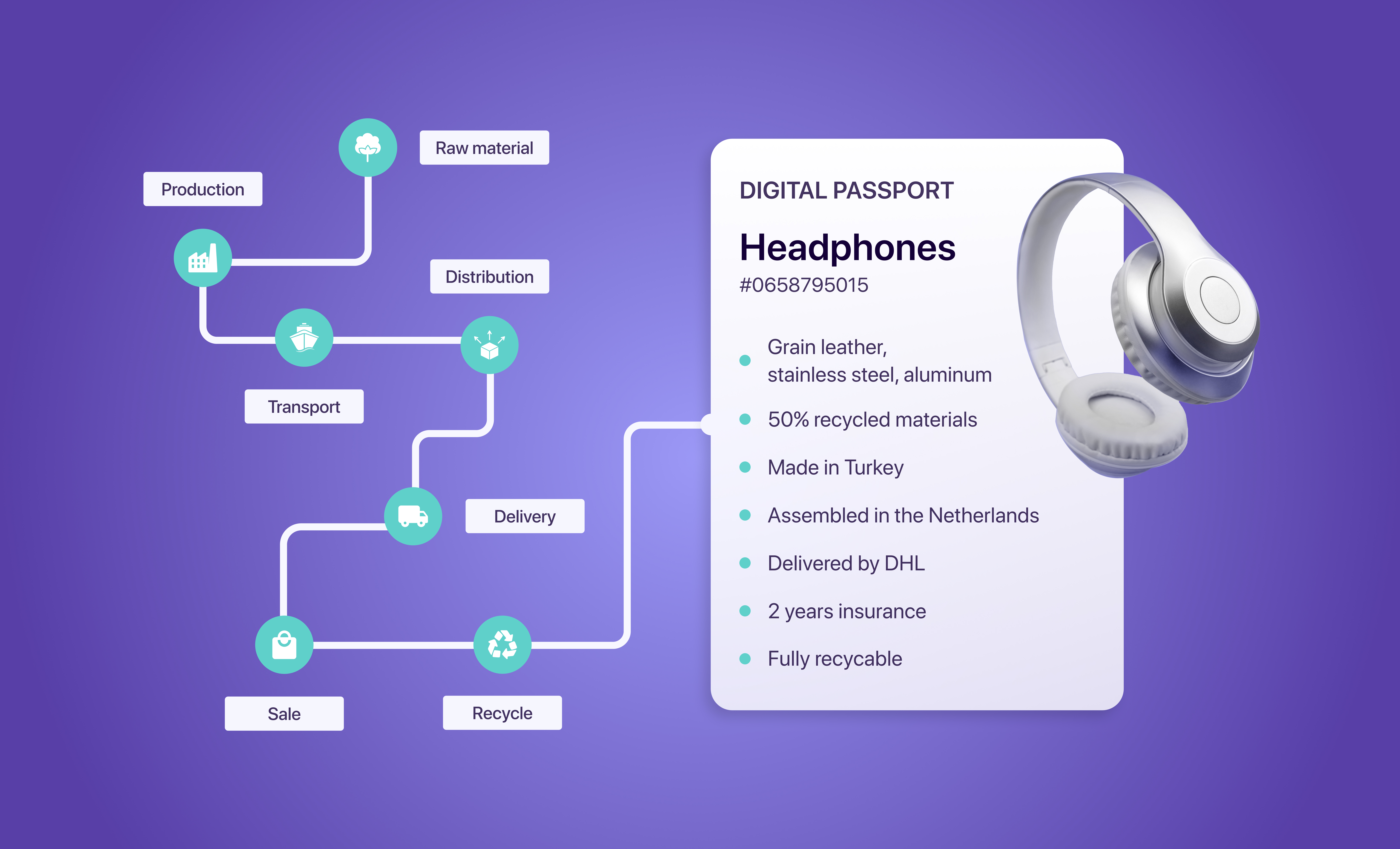
One notable example is the European Union's (EU) Digital Product Passports (DPP) regulation. This regulation emphasises the importance of transparency and traceability by requiring companies to provide detailed information about the lifecycle, environmental impact, and raw materials used to manufacture their physical products.
The DPP initiative is a pioneering step towards increasing consumer trust and making informed decisions. It exemplifies how regulations are driving full transparency and chain traceability, compelling businesses to not only adopt these practises voluntarily but also to ensure adherence through legal frameworks. Read more about DPP legislation here.
Consumer goods companies that embrace and implement transparent practises not only position themselves as sustainability leaders, but also as compliant organisations in a rapidly changing legal landscape. If you want to read more about DPP click here.
Companies in the consumer goods industry must prepare for a future in which transparency and traceability are not just recommended practises, but essential components of a thriving and sustainable business model. This article will delve into the significance of transparency and traceability, as well as the challenges that businesses will face when implementing these practises.
What is the difference between traceability and transparency in supply chain?
Transparency and traceability, while often interlinked, are different in supply chain management. Transparency is capturing and sharing overarching information throughout the supply chain. It facilitates companies to map their entire chain and ensure adherence to safety and sustainability protocols.
Traceability focuses on the meticulous data surrounding individual ingredients or components. It helps in tracking product origins and journeys, from the supply chain's inception to the end user. These concepts are fundamental when dealing with digital products. It establishes trust in the brand and increases the authenticity of virtual goods.
Ensuring ethical sourcing of materials and labor is a growing concern for consumers and regulatory bodies. Modern-day consumers are environmentally conscious and prefer sustainable and eco-friendly products. Businesses can position themselves as sustainable brands through transparency and traceability.
The importance of transparency and traceability for consumers
The importance of traceability and transparency for consumers has become an indispensable aspect of modern business. Some industries, particularly consumer goods and fashion, have been more impacted by this consumer behavior than others. Here's a detailed exploration of these critical concepts, their benefits, and examples:
Transparency
Transparency involves sharing details about the production process. That generally includes ethical considerations such as worker welfare, supplier information, and environmental impact. Customers increasingly favor brands that openly communicate about such details. It helps them form an emotional connection with the brand. A striking 65% of US shoppers prioritize transparent brands.
Transparency can help manage and monitor supply and distribution chains, filling gaps in knowledge and creating trust-based relationships.
The fashion brand Everlane is incredibly transparent about its carbon footprint, plastic use, and fabric choices. Its website details everything about its environmental initiatives and its shortcomings in achieving its goals. Customers enjoy this transparency, which speaks to the brand's commitment to its ambitions.
What are the steps to achieve product transparency?
Here are some things you should do to implement product transparency:
Gather precise information about different steps from product sourcing to selling. Also, collect pictures because most people love to see rather than read. Behind-the-scene photos of the people working on farms, factories, and transportation are great.
Create a team to handle transparency regulations and ensure adherence to set goals. You can also outsource this.
Write out exciting facts and detail the processes at each step in easy-to-understand language to go with the images.
Determine your carbon footprint, emissions, and waste during different stages of the product's cycle. Get accurate statistics that are verifiable.
Determine your business’s stance on recycling, commitment to sustainability, local economy support, and other related incentives.
What are the benefits of transparency?
Product transparency offers the following benefits:
Increases customer affinity and allegiance
Enhances businesses partnerships and consumer confidence
Allows brands to humanize supply chains and establish deeper connections with conscious consumers
Helps with product ownership mapping
Ensures accurate documentation of the origin of components and fabrics
In industries governed by regulations and standards, transparency ensures that digital products adhere to legal requirements. These can be related to product safety, environmental standards, and labeling.
By revealing a product's environmental impact, waste management and recycling become more efficient, reducing environmental harm.
Transparency in the development process allows stakeholders to see progress in real-time, identify bottlenecks, and make informed decisions.
Transparent practices and chain traceability contribute to a positive brand reputation.
Combats challenges of greenwashing (when brands claim to be sustainable and eco-friendly without actually being that)
Traceability
Traceability is closely related to transparency. It provides the means to follow a product through its lifecycle. Product traceability provides granular tracking, while transparency encompasses broader operations. Technologies like blockchain have been revolutionary, enhancing transparency and traceability in manufacturing processes. It ensures reliability, security, quality, and efficiency.
Over 70% of consumers value supply chain traceability, which builds loyalty and drives higher spending and positive reviews. Here is how you can make your products traceable:
Map out your supply chain and identify each stakeholder.
Understand the role of each member. Wisely choose your suppliers because they will either make or break your reputation as an eco-conscious brand.
Ensure each partner is on the same page regarding sustainability, ethical practices, and transparency.
Check if your raw material suppliers can provide data on their supply chains. Do your research on the provided data to ensure everything checks out.
Establish a code of conduct for your entire supply chain to ensure consistency across the board. This can include fair wage rules and waste management guidelines.
Ensure you have the financial resources and team to offer traceability services to your customers.
Keep communication channels open between your business, suppliers, customers, and support teams.
What are the different types of traceability?
For consumer goods companies, the most important types of traceability are:
Source Traceability: Establishing clear links from requirements to stakeholders who propose these requirements is crucial for understanding the origin and context of product demands.
Requirements Traceability: Creating links between dependent requirements ensures a comprehensive understanding of the interdependencies and expectations within the product specifications.
Design Traceability: Linking requirements to design helps maintain alignment between initial concepts and the final product's design, aiding in meeting consumer expectations.
Testing Traceability: Ensuring links between requirements and test cases guarantees thorough testing and validation of each requirement, enhancing product quality and reliability.
Quality Traceability: Maintaining links between requirements, design, testing, and implementation ensures consistent quality control throughout the product's development lifecycle.
Business Traceability: Establishing links between project requirements and the company' overall business goals ensures that the final product aligns with the company's broader objectives and strategies.
Traceability in fashion supply chain
The use of blockchain enhances traceability in fashion supply chains. It helps costumes understand where each fabric was sourced and if any was recycled. They can even trace if any fertilizers were used on the cotton farm, the manufacturing plant's energy consumption, and details of its transportation to the store.
The Fashion Transparency Index ranks the top fashion brands based on their level of supply chain product transparency and chain traceability. It helps consumers make conscious buying decisions. Ecofashion Corp is an apparel brand that puts QR codes on its clothes. Customers can scan it to trace the product from the farm to the store.
What are the benefits of traceability?
Traceability offers several benefits for customers and businesses, such as:
Companies can verify the authenticity of their products and prevent the circulation of counterfeit goods in the market.
Companies can track the environmental footprint of their products and report on sustainability initiatives.
Traceability allows developers and manufacturers to track the entire lifecycle of a digital product, thus ensuring quality.
Helps ensure the reliability of sustainability claims
Aids customers in understanding a product's lifecycle and making informed purchase decisions
It helps identify and address potential risks in the supply chain, such as disruptions, quality issues, or unethical practices.
Companies can use traceability to share the story of their products with consumers.
May promote sustainable and responsible practices, including recycling, contributing to the circular economy
Ensures responsible practices regarding human rights, labor, and environmental reliability
Enables businesses to gather data about the supply chain and product lifecycle. Analyzing this data provides insights that inform business decisions and strategies.
Importance of transparency and traceability for businesses in the EU
Fast fashion has a massive impact on the climate crisis. Hence, there is a need for sustainability initiatives such as sustainable supply chain management (SSCM), collaboration, investment in decarbonization, and product redesign.
In line with the European Green Deal's climate-neutral goal by 2050, the European Commission has propelled the Digital Product Passport (DPP) concept. The DPP is introduced as part of the Ecodesign for Sustainable Products Regulation (ESPR) to enhance sustainability and traceability across the value chain.
In simpler words, the EU will make transparency and traceability mandatory. Since the trend towards sustainability is growing, other regions may follow the EU's example and introduce similar regulations.
In the textile industry, the idea of the DPP aligns with the EU's strategy for sustainable textiles. Luxury brands like LVMH are already utilizing DPPs for authenticity and origin verification.
Learn more about how DPP regulation will affect your industry here.
Common challenges with embedding transparency and traceability
Implementing traceability and transparency brings incredible advantages to brands but the consumer goods industry has complex supply chains. That makes it difficult to embed transparency and traceability into products. Here are some common challenges companies may face:
1. Data collection and integration
Gathering accurate and relevant data from various sources can be difficult. Integrating data across systems, suppliers, and partners into a cohesive traceability framework requires robust technology and data management practices.
With Layerise, you can gather extensive details from your ERP and PIM systems regarding your products and supply chain. This enables you to build a thorough and complete digital product passport, encompassing all essential information, which can then be readily shared with your customers.
2. Ensuring data accuracy and reliability
Relying on accurate data is crucial for traceability. Inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to incorrect conclusions and decisions. However, ensuring accuracy is time-consuming and expensive, and many businesses cannot afford it.
3. Maintaining data security and privacy
Sharing data across the supply chain requires careful data security and privacy consideration. Businesses must balance maintaining transparency and protecting sensitive information from unauthorized users.
4. Supplier collaboration
Achieving traceability requires the collaboration of suppliers and partners. Ensuring that all stakeholders follow the same standards and protocols can be challenging, more so if the process is international.
5. Legacy systems
Companies may have legacy systems lacking the necessary capabilities for comprehensive traceability. Again, integrating traceability into these systems or migrating to new ones can be resource-intensive, which many businesses cannot afford.
6. High costs
Implementing traceability technologies, such as RFID, blockchain, or data analytics software, requires financial investments and skilled resources for development, integration, and maintenance.
7. Overhaul of business processes
Embedding traceability may require changes in processes and practices throughout the organization and its partners. Your employees need to adapt to new ways of working and using technology. Building a culture of transparency and collaboration across a supply chain may be difficult.
8. Consumer education
Transparency efforts may involve sharing complex information with consumers. Communicating this information clearly and understandably may require experts and a legal team, which not every business has.
9. Legal and regulatory compliance
Different regions have varying regulations and standards regarding data privacy, product labeling, and transparency. Ensuring compliance across borders is a known challenge.
10. Scaling up
Embedding transparency and traceability for a few products might be manageable. However, scaling up to cover a wide range of products, potential customers and supply chain partners requires careful planning.
How Layerise can help you with DPP
Transparency and traceability are becoming pivotal in modern consumer relationships, particularly in fashion-related industries. However, the complex tiered structure of the fashion supply chain poses challenges, as discussed above. These include issues in tracking impact, holding vendors accountable, and complicating sustainability.
Layerise offers a cost-effective solution to those challenges in the form of DPPs. Here's an introduction to creating your product's DDP using Layerise:
Understand the information required in the DPP, such as material sourcing information and authenticity.
Gather and import data from your systems into Layerise. This will allow you to easily share all the product information with your customers.
Set data access, sharing, and authorization rules.
Implement QR code technology on your products to make the DPP easily accessible. Customers will access the information of the specific product through an identification number that will be required at the time of the product registration.
Update data or add information as required. Layerise's DPPs are flexible and can be changed anytime by authorized users.

Layerise enables consumer good brands to provide updated and measurable product information. An example is the Danish brand Samsøe Samsøe, which adopted QR codes technology to boost circular economy. That enhanced its end-user experience with seamless access to online resale platforms.
You can customize the Layerise platform according to your business needs. The DPPs you create here can reflect everything you want, such as brand name, material quality, facility location, carbon footprint, recycling instruction, and more.
Integrating transparency and traceability within consumer goods firms is more than a business strategy. It is an ethical imperative for societal, environmental, and economic sustainability. Join the movement now and sign up with Layerise to create DPPs.
Learn more about how DPP regulation will affect your industry here.
Learn how to collect valuable insights on your customers to sell even more.

How to Turn a New Obligation into a Growth with Layerise
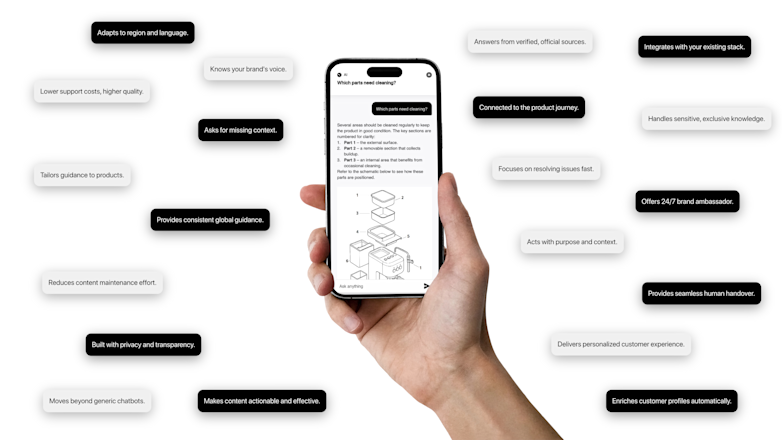
A trusted, brand-safe AI assistant that knows your products, your customers and your content.