Data collection is a sensitive subject. Nowadays, anyone can access your data just by clicking a button. Some fear that unauthorized parties or organizations will access or misuse their data, leading to identity theft or fraud. Others are worried about cyberattacks, such as hacking, phishing, or malware, which can result in data breaches and exposure to sensitive information.
There is a general concern about having little control over how online companies and platforms collect, use, or share their data. That leads to a loss of privacy and autonomy over their personal information. Violations are costly. A fine of €10 million was imposed on Google by AEDP, Spain's data protection agency, for sharing the personal information of EU citizens who requested the erasure of their data with the Lumen Project. A data breach at Cosmote Mobile Telecommunications, Greece's largest mobile operator, led to its customers' data being stolen. The company was found not to have implemented proper data protection measures. The Hellenic Data Protection Authority fined it €6 million.
How can business collect valuable information about customers while making them more comfortable to share their data? It remains a key question for not just companies but also governments across the world. It was this concern that led to the development of the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which came into effect in May 2018. The GDPR aims to establish a framework for the protection of personal data, giving individuals greater control over their information and placing obligations on organizations to handle data responsibly and securely.
In this article, we will delve into the impact of GDPR regulations on your ability to capture customer data. We will provide you with a comprehensive understanding of the key aspects and implications of the GDPR in relation to data collection.
General Data Protection Regulation: What is it?
Let's start with the basics. The General Data Protection Regulation – GDPR is a massive and thorough set of data privacy rules. It requires any business or organization operating within the European Union (EU) to safeguard people's data and privacy. And get this - it's so good that it has set the standard for data privacy and protection worldwide. The Information Commissioner's Office is responsible for interpreting and enforcing the GDPR.
It has completely transformed how businesses handle personal data across all industries. Consumers now have more control over how companies collect and use their data. People can now decide who gets to collect their data and when it's collected. They also determine how companies can use the information. The GDPR has even given people the right to tell businesses to delete their data altogether. Why is this a big deal? It puts the power back into the hands of individuals when it comes to their data. The regulation is all about protecting people's privacy and ensuring that businesses do everything possible to keep personal data safe.
The GDPR has effectively established protective measures and protocols to ensure companies can't collect or utilize data from their consumers and potential clients without clear, straightforward disclosures. It has also imposed high penalties and fines for violations or data breaches.
Companies need to show that they're sticking to the rules and taking good care of their customer's data as required by GDPR. They should be open about the data they acquire, their reasons for gathering it, and the security measures they use to ensure there is no violation of data collection.
Even though this originated in Europe, it's implemented everywhere since data concerns are not limited to that part of the world. Companies that generate business by providing products or services in the EU are subject to this regulation. Regardless of whether a company is physically present in Europe, it must comply with this legislation as long as it conducts business here. Therefore, it affects many international companies, which is good as they have to implement it for the entire company, benefitting people in other parts of the world that gain business from them.
Even though it is pretty exciting to talk about GDPR compliance, we need to know what qualifies as personal data. By doing so, we better understand what and why GDPR was created and implemented.
Data stipulated under GDPR compliance
The data GDPR is very keen on is personal data. Even though what is considered personal data can waver from place to place and under different laws, GDPR has done an excellent job of defining personal data.
This data may consist of the following:
Basic personal information like the name, address, phone number, and email address.
Web data is collected through online tracking technologies such as cookies, IP addresses, device identifiers, and RFID tags.
Sensitive personal information, whether it is health data, information on their race or ethnicity, and even sexual orientation.
Financial information includes credit card numbers, bank account information, and other financial details.
Employment information like employment history, job titles, and salary information.
Communication data, including phone call records, email messages, and chat logs.
Identification numbers include social security, passport, and driver's license numbers.
Does GDPR apply to your company?
If a company collects data from individuals in the EU, whether or not they are citizens there, they are automatically bound to comply with GDPR. It also applies to companies that collect and keep data from EU data subjects, regardless of having an EU base or even if you are not bound by law to pay taxes in the EU, so long as it is a region from which you collect data.
So companies that wish not to be bound by this regulation must block access to sites in the EU to avoid accidental EU data collection, which can unintentionally land the company into problems.
Nonetheless, it is an excellent principle to follow by companies whether GDPR applies to them. That is because customers require companies to uphold these regulations in some form to have their trust and loyalty.
Why was GDPR introduced?
There are eight guiding principles stipulated by GDPR for handling personal data (outlined in Article 5). These serve as the base on which GDPR works. These are supposed to form a blueprint to guide the operations of the companies that adhere to it not and not merely stringent laws.
Companies must show that the customer was responsible for requesting and receiving information about the company and not because the company targeted them. It can mean that the company may have to redesign its forms and questionnaires to be a state that is in keeping with GDPR. On top of that, companies cannot refuse to provide information by blocking access to their website because a client would not want their personal information to be collected.
8 GDPR Rights of Individuals
These rights give individuals control over their personal information. They allow people to access, modify, and delete their data and object to its use in certain circumstances.
They include:
Right to be informed: Individuals must know how their data is processed.·
Right of access: They should be able to access their data and information about how it is being processed.
Right to rectification: Individuals can request the correction of inaccurate or incomplete personal data.
Right to erasure: Individuals can request the deletion of their data under certain circumstances.
Right to restrict processing: They can restrict the processing of their data under certain circumstances.
Right to data portability: They can receive their data in a structured, commonly used, and machine-readable format and transmit it to another controller.
Right to object: Individuals can object to processing their data under certain circumstances.
Rights related to automated decision-making and profiling: Individuals have the right to object to automated decision-making and profiling and to request human intervention in such cases.
How does GDPR affect your data capture activities?
GDPR aims to bring back control to the customers over their data. It involves anything about a person, like, name, photo, email address, bank details, location details, medical information, or computer IP address. GDPR applies to all companies that do business with European Union residents, including all technical processing companies that act as intermediaries between the sellers and customers to process the information on behalf of the customers.
When it comes to consumer involvement, large organizations are mostly affected. A good example is Facebook. From its pitfalls, companies have learned to cease using outdated opt-out procedures or implicit consent. Facebook was forced to adopt an opt-in consent procedure instead. That is because the legislation provided that the user's inactivity cannot be interpreted as consent to data capture. That's one of the ways organizations try to find loopholes in data capture.
Therefore, the value of GDPR is mainly appreciated in a company's consent system. It stops companies from obtaining personal data that is not legally justified, which excludes anything that is implied. It has to be clearly stated.
The GDPR's Article 7 addresses "conditions for consent."
Where the processing is based on consent, the controller shall be able to demonstrate that the data subject has consented to processing their data.
Suppose the data subject's consent is given in the context of a written declaration that also concerns other matters. In that case, the request for consent shall be presented in a manner that is distinguishable from the other matters in an intelligible and easily accessible form, using clear and plain language. Any part of such a declaration that constitutes an infringement of this regulation shall not be binding.
The data subject shall have the right to withdraw their consent at any time. The withdrawal of consent shall not affect the lawfulness of processing based on consent before its withdrawal. Before giving consent, the data subject shall be informed thereof. It shall be as easy to withdraw as to give consent.
When assessing whether consent is freely given, utmost account shall be taken of whether, among other things, the performance of a contract, including the provision of a service, is conditional on consent to the processing of personal data that is not necessary for the performance of that contract.
It ensures that the consumer is aware their data is being collected, what it is being used for, that they consented to it knowingly, and should there be inactivity on the consumer's part, the company should ask for approval from the consumer.
Some of the principles that uphold the conditions of consent include:
Integrity and transparency – To facilitate awareness of how one's data is being managed, it is paramount for the reason to be disclosed concisely. The data subject should fully understand how their information is gathered and processed.
Purpose limitation – This principle, in particular, upholds that data cannot be stored and used for purposes other than those stated initially to the individual (data subject) in the disclosure at the initial point of contact. It works to stop companies from selling personal data as if they own rights to it.
Data minimization – This limits data collection to what is necessary. A company is urged to find the essential information from the data subject to give them the service it offers.
Storage limitation requires companies to state that the data subject understands how long they plan to keep their data and that they will get rid of it after it has served its purpose.
Accuracy – It is essential that the data gathered is accurate. It ensures that the data being used belongs solely to the data subject. Platforms like Layerise enable you to accurately collect 1st party customer data for your consumer brand, with strict conformity with GDPR. You can then use this data to grow your conversions through targeted marketing and provide personalized assistance. Book a demo here.
Confidentiality – Any personal information collected is considered sensitive and should be treated as such. It should be processed based on only what is essential, and only a few should have the privilege to access it. Limited to only those that require it to do their work duties. Companies enhance confidentiality by keeping the data subject's privacy as a core principle of the company and using their data in a manner sensitive to the customer.
Accountability – According to the ICO website, a company that has been given the privilege to control peoples' data must be accountable for how they are using this data. They should always have competent people to manage it and ones who are fully trained in what GDPR compliance means.
How to meet GDPR conditions
After highlighting the fundamental principles of GDPR and why it is crucial to adhere to the guidelines, it is essential to know what steps can be taken to meet those regulations and become GDPR compliant, as well as the penalties for breaching these guidelines.
1. Take charge of your data safety: Create a data protection office
A Data Protection Officer (DPO) 's work is to ensure that the company is fully GDPR-compliant and be the point of contact between the company and the data subject(s). The DPO should also analyze and perform data protection checks to ensure the company complies with the GDPR.
2. Understand the difference between opt-in and opt-out consent
A key aspect of GDPR is allowing customers to decide whether to share their personal information with a company.
Two types of consent matter: opt-in and opt-out.
With opt-in, the consumer actively consents by taking an explicit action to agree.
For opt-out, the consumer must stop the company from using their data, even though they might have previously consented.
Under GDPR, the default option for consent should be opt-in for most activities. Companies must ensure that consumers consent before using their data. It is essential for companies to understand the difference between opt-in and opt-out and to use the appropriate type of consent for each situation.
3. Get transparent: Tell website visitors how you'll use their data
Users must be immediately informed of the use of cookies and given the option to accept or decline, including those that are strictly necessary and their use on the website. Users can then decide whether to accept or reject the usage of cookies in an informed manner.
4. Assign a compliance representative for your organization
It is essential for any company that does business in the EU and lacks a physical office in the region to hire a GDPR representative there. It facilitates adherence to GDPR for residents in the EU. This representative must be the company's liaison for all inquiries about personal data collection. The representative's office (different from the DPO’s) would facilitate communication between the company and supervisory authorities under the GDPR.
5. Don't get caught with your privacy down: Continuously assess risks and shortcomings
Conducting risk analyses is essential for companies as it enables them to find gaps that some of their employees and cybercriminals could use to sabotage personal data. It involves looking for potential dangers that could lead to customers' private information being illegally obtained and evaluating how likely these risks will happen.
The ISO 27001 standard provides guidelines on how to evaluate security risks. It states that the GDPR requires companies to conduct a GAP analysis to assess their compliance with the regulation. This technique involves evaluating a company's information systems and online presence to identify gaps between its current practices and GDPR requirements. The GAP analysis will help companies understand whether they are meeting GDPR standards and, if there are issues, determine the steps to improve their compliance. Many companies achieve this by updating their current risk mitigation measures. Following the ISO 27001 standard and performing GAP analysis ensures your company meets GDPR requirements and keeps your customer's data secure.
6. Comply with Data Subject Access Requests
The GDPR grants European Union citizens the right to obtain the personal data that companies have gathered and understand how it is used. They do this by submitting a data subject access request (DSAR). Companies must comply with such requests and furnish a copy of their personal information about the concerned individual.
The information provided should include the following:
The legal grounds for having that data;
How long will it be kept;
Who it is shared with.
You can use data mapping to ensure that you have collected all the required data and can track how it moves between internal departments and systems. It's a checklist tool that helps companies comply with regulations and maintain an accurate record of their data.
7. Keep personal information safe with data processing agreements
As long as you collect personal data, you should take proactive measures to protect it. If you hire third-party contractors to process this data, you must ensure that these parties comply with GDPR. To achieve this, use a Data Processing Agreement legally binding the data controller and processor. This agreement outlines the specifics of data processing and how the two parties are related. It also protects data subjects, as any misuse of their personal information can be prosecuted by law.
Comply with data usage regulations: Because ignorance isn't bliss
The GDPR compliance process, even though very important, is not easy to figure out. However, it profits any company to remember that these regulations safeguard consumers, which the company can be on the receiving end. GDPR intends to protect our personal information and provide more authority over its use. The law is ambitious and extensive because our online information is easily stolen or exploited.
Regardless, it is difficult for all enterprises to comply with the GDPR because it is easy to access personal data and justify that it is essential for the operation and expanding companies. As a company grows, it must train new and current employees yearly to ensure necessary compliance.
These guidelines are here to help your organization get compliant with data regulations efficiently and effectively. It's way cheaper than hiring a battery of lawyers to protect your company from all angles, and your customers also get to rest assured that their data is safe.
Penalties for GDPR violations
The GDPR introduced some of the harshest penalties for a breach of any data protection law in the world, with penalties as high as €20 million or 4% of the company's previous worldwide annual revenue. An excellent example of this is Amazon which, in 2021, was fined $888 million for a GDPR violation.
These severe penalties offer the GDPR significant sway in mandating adherence to the rules, ensuring that all data subjects have consented, and reducing the possibility of infringing personal data.
The EU is very serious when it comes to protecting personal information. If a company does not abide by its rules, it risks hefty fines, losing potential customers, and even losing brand credibility.
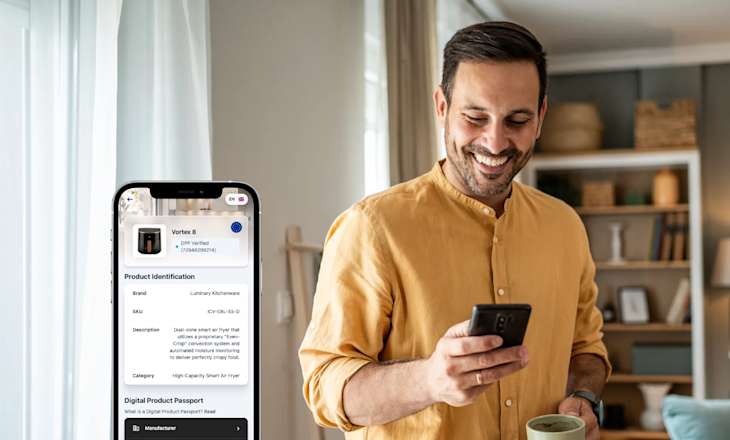
How to collect customer data GDPR compliant
Layerise is a platform that enables companies to collect customer data while ensuring compliance with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). With the help of QR code technology, Layerise provides a convenient way for you to connect with your existing customers. By offering exclusive benefits and access to information related to their newly purchased product, customers are motivated to initiate the registration process. As part of this process, they are requested to share their information, which allows for a superior and personalized customer experience.
The first-party data collected during the onboarding process can be used throughout the entire product ownership cycle. This data can include basic customer information as well as more detailed data on purchase history, behavior, and preferences. What sets Layerise apart is its ability to track and measure customer purchase intent, that help businesses identify which customers are most likely to make a purchase and target them with relevant marketing messages. Read more about it here.
To conclude, with Layerise companies can enhance their understanding of customer needs, improve their marketing strategies, and ultimately drive sales. By prioritizing data privacy and compliance with GDPR regulations, Layerise empowers businesses to collect and utilize customer data responsibly, while fostering strong and personalized customer relationships.
Learn how to collect valuable insights on your customers to sell even more.

How to Turn a New Obligation into a Growth with Layerise
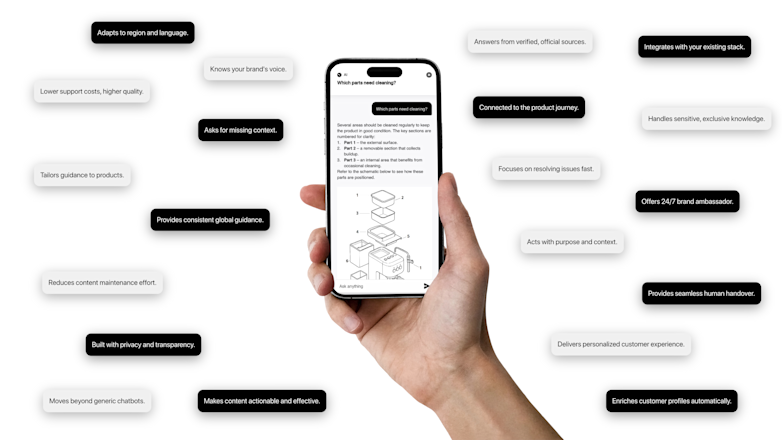
A trusted, brand-safe AI assistant that knows your products, your customers and your content.